In August 2024, an unexpected seismic event shook the United Arab Emirates (UAE), marking a significant moment in the nation’s modern history. The earthquake, with its epicenter located in the region, brought with it a wave of both concern and resilience. This article delves into the details of the earthquake, its impact, and the response from the UAE and the international community.
The Earthquake: An Overview
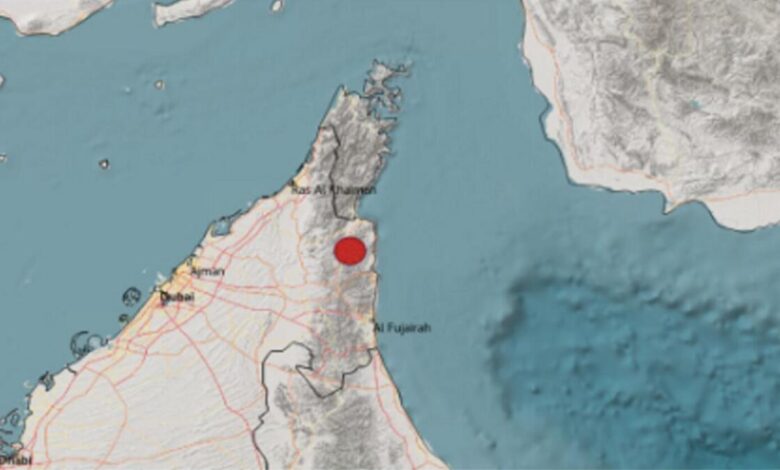
On August 15, 2024, the UAE experienced a notable earthquake that registered a magnitude of 5.8 on the Richter scale. The tremor struck at approximately 2:45 PM local time, with its epicenter located in the Al Ain region, near the border with Oman. This region, while not typically known for high seismic activity, experienced a jolt that was felt across several major cities, including Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and Sharjah.
Seismic Details:
- Magnitude: 5.8
- Depth: 10 kilometers (6.2 miles)
- Epicenter: Al Ain region, UAE
- Impact Radius: Felt in major cities across the UAE and parts of northern Oman.
Immediate Impact and Damage
The earthquake caused varying degrees of damage across the UAE, with Al Ain being the most affected area. The impact was significant but not catastrophic, with infrastructure, residential, and commercial properties sustaining damage.
Key Areas Affected:
- Al Ain: Several buildings, including older structures, experienced cracks and partial collapses. The local infrastructure, such as roads and bridges, faced minor to moderate damage.
- Dubai: The skyscrapers and modern buildings largely withstood the quake, but there were reports of minor structural issues and some office evacuations.
- Abu Dhabi: Similar to Dubai, the capital city saw minimal structural damage but experienced brief disruptions in services.
The earthquake prompted immediate concerns about safety and preparedness, leading to emergency responses and assessments of the damage.
Response and Recovery Efforts
The response to the earthquake was swift and coordinated, involving local, national, and international efforts. The UAE government, known for its robust disaster management strategies, mobilized resources quickly to address the situation.
Government Actions:
- Emergency Services: Local emergency services were deployed to assess damage, provide medical assistance, and ensure public safety. The UAE Civil Defence and police were actively involved in managing the response.
- Infrastructure Repair: Initial assessments focused on repairing critical infrastructure, including roads and bridges, to ensure connectivity and safety.
- Public Safety: The government issued safety advisories and conducted building inspections to prevent further risks and ensure that structures were safe for occupancy.
International Assistance:
The international community responded with solidarity, offering support and assistance to the UAE. Countries and organizations provided aid in various forms:
- Humanitarian Aid: Several nations, including the United States, the United Kingdom, and neighboring Gulf countries, offered humanitarian aid and support in the form of rescue teams and relief supplies.
- Technical Assistance: Experts in seismic engineering and disaster management were brought in to assist with damage assessments and recovery plans.
Impact on Daily Life and Economy
The earthquake had a notable impact on daily life and economic activities in the affected regions. While the damage was not catastrophic, it disrupted routine activities and highlighted areas for improvement in disaster preparedness.
Daily Life:
- Disruptions: Public services, including transportation and utilities, experienced temporary disruptions. Some areas faced power outages and water supply issues.
- Safety Measures: Residents were advised to follow safety protocols, including avoiding damaged buildings and staying informed through official channels.
Economic Impact:
- Property Damage: The economic cost of property damage was substantial but manageable. Insurance claims and repair costs were expected to be significant, particularly in older and less resilient structures.
- Business Disruptions: Some businesses faced interruptions due to building damage or reduced foot traffic. However, the economic impact was mitigated by the swift recovery efforts and the overall resilience of the UAE’s economy.
Lessons Learned and Future Preparedness
The earthquake served as a critical reminder of the importance of disaster preparedness and resilience. While the UAE is not typically associated with high seismic activity, the event prompted a reevaluation of existing safety measures and protocols.
Key Lessons:
- Building Codes and Standards: The importance of adhering to rigorous building codes and standards was underscored. The earthquake highlighted the need for continuous evaluation and updating of construction practices to ensure structural integrity.
- Emergency Preparedness: The response demonstrated the effectiveness of emergency preparedness plans but also highlighted areas for improvement, such as public awareness and community resilience training.
Future Preparedness:
- Infrastructure Investment: Investment in infrastructure resilience and disaster-resistant technologies is expected to increase. Efforts will focus on strengthening buildings, bridges, and critical facilities.
- Public Education: Increased emphasis on public education regarding earthquake preparedness and safety measures will be a priority. Schools, businesses, and communities will be encouraged to participate in preparedness drills and educational programs.




One Comment